Medications Info
Dexedrine Medication and Prescription Guide
Dexedrine Medication and Prescription
Dexedrine is a well-known prescription medication that has been used for decades to help manage conditions like Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. It belongs to a class of drugs known as central nervous system (CNS) stimulants, which work by increasing certain chemical activity in the brain that controls attention, focus, and impulse control.
In recent years, Dexedrine has remained an important treatment option, especially for people who do not respond well to other ADHD medications. Understanding how it works, how it’s prescribed, and what to expect can help patients and families use it safely and effectively.
What Is Dexedrine?
Dexedrine is the brand name for dextroamphetamine, a stimulant that affects chemicals in the brain related to focus and behavior. It has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for over 50 years and is available in both immediate-release and extended-release forms.
-
Generic Name: Dextroamphetamine sulfate
-
Drug Class: Central nervous system stimulant
-
Schedule: Controlled substance (Schedule II) due to potential for misuse or dependence
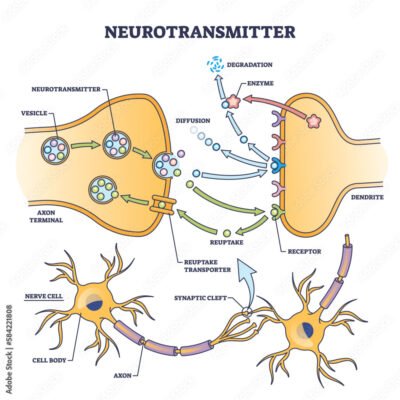
Dexedrine increases levels of dopamine and norepinephrine, neurotransmitters that influence alertness, energy, and mood. When used correctly, it helps people with ADHD manage symptoms like inattention, impulsivity, and restlessness.
How Dexedrine Works
Dexedrine works by stimulating the release of dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain while also preventing their reabsorption. This process enhances communication between brain cells and helps maintain focus and alertness.
For ADHD
In individuals with ADHD, Dexedrine helps balance underactive brain areas that control attention and executive function. This often results in:
-
Better focus and task completion
-
Decreased impulsivity
-
Improved academic or work performance
For Narcolepsy
For people with narcolepsy, Dexedrine promotes wakefulness by reducing excessive daytime sleepiness and improving alertness throughout the day.
Prescription and Dosage
Dexedrine must always be prescribed by a licensed healthcare provider, as its dosage and timing vary depending on the patient’s age, condition, and response to treatment.
Typical Dosages
-
Children (6 years and older): Usually start with 5 mg once or twice a day.
-
Adults: May range from 5 mg to 60 mg daily, divided into smaller doses.
-
Extended-Release (Spansule): Taken once daily in the morning for long-lasting effects.
Important Notes
-
Dexedrine should be taken early in the day to avoid insomnia.
-
It can be taken with or without food.
-
Never increase or skip doses without consulting your doctor.
Because Dexedrine is a controlled substance, prescriptions often require regular check-ins with the prescriber and cannot be refilled automatically.

Possible Side Effects
Like most stimulant medications, Dexedrine can cause side effects, especially during the early stages of treatment or when dosages are adjusted.
Common Side Effects
-
Loss of appetite
-
Dry mouth
-
Difficulty sleeping
-
Increased heart rate
-
Headache
-
Nervousness
Less Common but Serious Side Effects
-
Elevated blood pressure
-
Mood changes or aggression
-
Dizziness or chest pain
-
Unexplained fainting
-
Hallucinations (in rare cases)
Patients should contact their healthcare provider if side effects are severe or persistent. It’s also crucial to discuss any history of heart disease, anxiety disorders, or substance misuse before starting Dexedrine. You can now get dexedrine online from Canada with a single click.
Safety, Warnings, and Interactions
Dexedrine is powerful and effective but should always be used responsibly. Misuse can lead to dependency or cardiovascular problems.
Key Safety Tips
-
Avoid alcohol while taking Dexedrine.
-
Don’t mix with other stimulants or antidepressants unless prescribed together.
-
Store medication safely away from children or anyone it’s not prescribed for.
-
Regularly monitor blood pressure and heart rate.
It’s also important to note that stopping Dexedrine suddenly can cause withdrawal symptoms such as fatigue or depression. Always taper under medical supervision.

Alternatives and Comparisons
Dexedrine isn’t the only stimulant used for ADHD or narcolepsy. Other medications with similar effects include:
-
Adderall (amphetamine and dextroamphetamine) – broader formulation, similar function.
-
Vyvanse (lisdexamfetamine) – longer-acting and often smoother in effect.
-
Ritalin (methylphenidate) – a different stimulant class that works on dopamine but has a shorter duration.
Choosing between them depends on the individual’s body chemistry, medical history, and lifestyle. A doctor can help determine which one offers the best results with the fewest side effects.